Java batch processing with JobRunr
Discover the power of Java batch processing with JobRunr — a modern, user-friendly solution for distributed job management.
1. Introduction to Java batch processing and JobRunr
Java batch processing refers to the execution of a series of tasks or jobs without human intervention. These tasks can be processed sequentially or concurrently, and are often used for data-intensive operations, such as data transformation, report generation, document generation, image analysis, or database maintenance.
JobRunr is a modern, open-source Java library that simplifies batch processing by providing a distributed, background job processing system with a built-in dashboard for monitoring and managing jobs.
2. JobRunr vs Spring Batch
JobRunr and Spring Batch are both well-regarded solutions for managing batch processing in Java applications, each with its unique strengths. JobRunr offers simplicity and ease of use, enabling developers to set up and manage batch processing tasks without extensive configuration. Its distributed processing capabilities allow applications to do parallel processing and scale effectively, ensuring better resource utilization and quicker job execution. Additionally, the built-in dashboard provides real-time job monitoring and management, offering valuable insights into job performance in a user-friendly manner.
While Spring Batch is known for its comprehensive set of features and integrations with other Spring components, it might be more complex and harder to configure compared to JobRunr. Spring Batch is an excellent choice for applications that have ETL (Extraction, Transformation and Load) needs, but for those seeking a more lightweight and modern approach to batch processing, JobRunr stands out.
Choosing between JobRunr and Spring Batch depends on the specific requirements and preferences of your project. JobRunr offers a streamlined, efficient batch processing solution with an emphasis on distributed processing and an intuitive dashboard, making it a strong contender for developers looking for an easy-to-use and powerful batch processing library. It also integrates well with Spring Boot making it an excellent choice and alternative for Spring Batch.
3. Advantages of using JobRunr for batch processing
JobRunr offers several advantages over traditional batch processing systems:
3.1. Distributed processing
JobRunr can distribute jobs across multiple nodes, allowing for better resource utilization and faster job execution. This is particularly useful for large-scale applications that require high throughput and low latency.
3.2. Background job processing
JobRunr enables the execution of long-running jobs in the background, preventing them from blocking the main application thread. This improves application responsiveness and ensures a better user experience.
3.3. Built-in dashboard
JobRunr includes a built-in dashboard that provides real-time information about job status, progress, and performance. This allows developers and system administrators to monitor and manage jobs with ease.
4. Setting up JobRunr in a Java project
4.1. Adding dependencies
To start using JobRunr in your Java project, add the following dependencies to your build configuration (Maven or Gradle):
<!-- Maven -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jobrunr</groupId>
<artifactId>jobrunr</artifactId>
<version>6.1.3</version>
</dependency>
4.2. Configuring JobRunr
Next, configure JobRunr by means of the Fluent API. JobRunr supports a lot of SQL and NoSQL databases but for the sake of this example, we will use the InMemoryStorageProvider:
JobRunr.configure()
.useStorageProvider(new InMemoryStorageProvider())
.useBackgroundJobServer()
.useDashboard()
.initialize();
5. Creating and scheduling jobs with JobRunr
5.1. Defining a job
A job in JobRunr is defined as a Java method or lambda expression that contains the logic to be executed. To define a job, create a class with a method that represents the task:
public class MyJob {
public void performTask() {
// Your job logic goes here
}
}
5.2. Scheduling a job
To schedule a job with JobRunr, use the JobScheduler instance and provide the job definition:
jobScheduler.<MyJob>enqueue(x -> x.performTask());
6. Job processing with JobRunr
6.1. Job retries
JobRunr automatically retries failed jobs based on a configurable retry policy. You can customize the number of retries on a per job basis:
public class MyJob {
@Job(name="My Batch Job", retries=3)
public void performTask() {
// Your job logic goes here
}
}
For more configuration options, feel free to check the docs.
6.2. Job prioritization
Using JobRunr Pro, you can assign different priorities to jobs, ensuring that higher-priority jobs are executed before lower-priority ones:public class MyJob {
@Job(name="My Batch Job", queue = HighPrioQueue)
public void performTask() {
// Your job logic goes here
}
}
6.3. Complex workflows
Another feature of JobRunr Pro is that you can create complex workflows that match your business processes:public void createArchiveAndNotify(String folder) {
jobScheduler
.enqueue(() -> archiveService.createArchive(folder))
.continueWith(() -> notifyService.notifyViaSlack("ops-team", "The following folder was archived: " + folder))
}
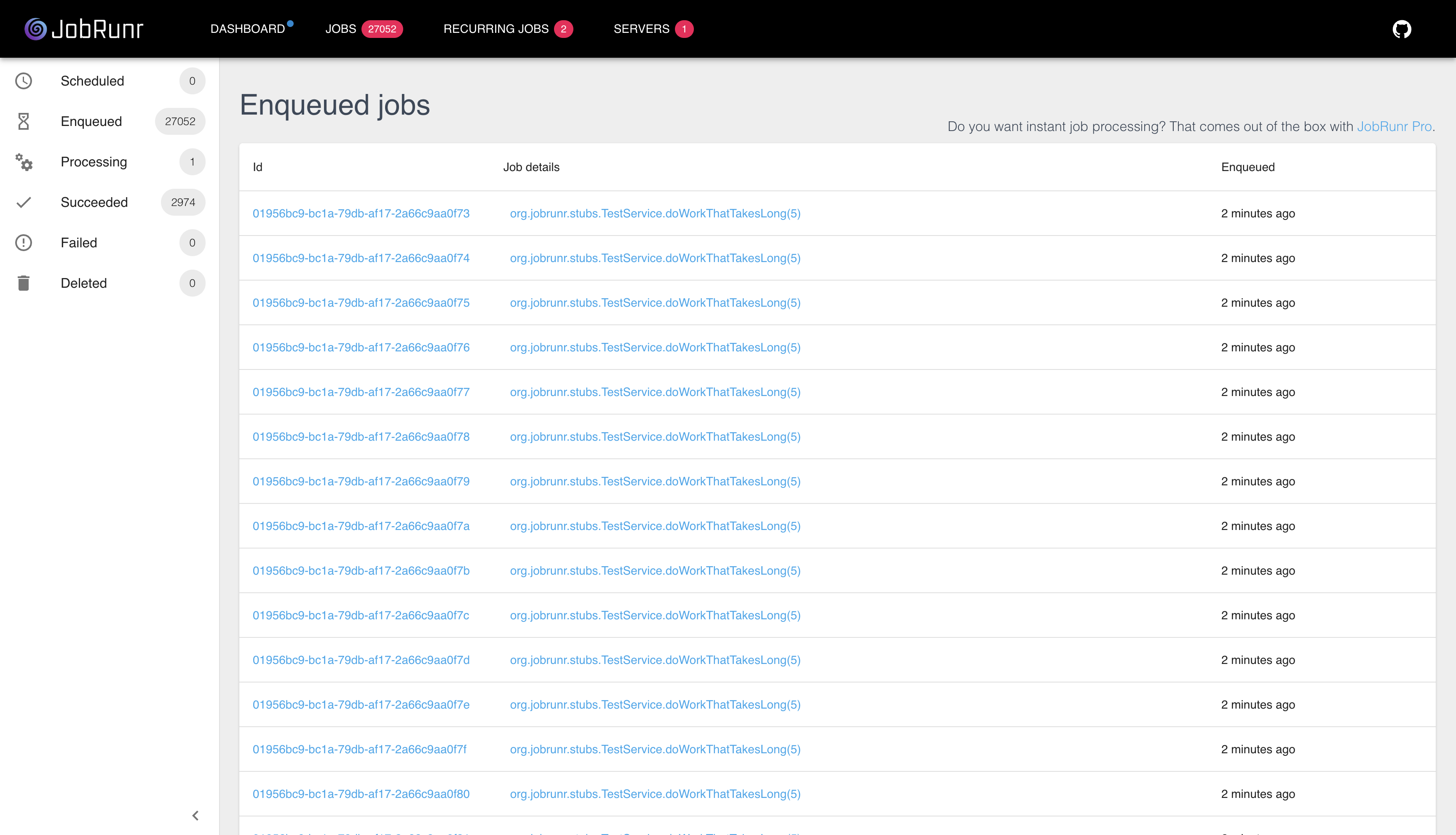
7. Monitoring and managing jobs through the JobRunr dashboard
7.1. Accessing the dashboard
JobRunr comes with an embedded dashboard (which is disabled by default). To access the JobRunr dashboard, start the built-in web server and navigate to the dashboard URL: http://localhost:8000.
7.2. Analyzing job performance
The JobRunr Dashboard provides various metrics and visualizations to help you analyze job performance, such as job duration, success rate, and throughput. Use this information to optimize your jobs and improve overall system performance.
8. Conclusion
Java batch processing with JobRunr offers a modern and powerful solution for managing background jobs in Java applications. With its distributed processing capabilities, built-in dashboard, and flexible configuration options, JobRunr simplifies job scheduling, execution, and monitoring, allowing developers to focus on their application’s core functionality.